前端开发 众所周知,前端三剑客(htm、css、JavaScript)是一个网页不可或缺的元素,本篇博客记录学习前端三件套的历程。
HTML html里面有很多标签,下面来逐一介绍
HTML标签 <!DOCTYPE html > HTML 文档的文档类型声明<html > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 1级标题 </h1 > <h2 > 2级标题 </h2 > ... <h6 > 6级标题 </h6 > </body >
编码(head) 定义用UTF-8来对字符进行编码
title(head) title标签是显示在网页的title位置
多级标题(body) <body > <h1 > 1级标题 </h1 > <h2 > 2级标题 </h2 > ... <h6 > 6级标题 </h6 > </body >
用<h?>标签来表示?级标题
div和span(body) <div > test</div > <span > test</span >
用<div>表示块级标签,包裹的内容占一行<span>表示行内标签/内联标签,字体多大占多少
上述的多级标题默认为块级标签,一个占一行
超链接(body) <a href ="https://baidu.com" > 点击跳转</a >
页面会出现一个蓝色字体的点击跳转字样,点击之后就会跳转到baidu.com
如果想跳转到自己的网页,可以只写相对路径,例如
<a href ="/login" > 点击登录</a >
这样实现的是当前页面跳转,如果想新建标签页跳转,只需添加target关键字
<a href ="https://baidu.com" target ="_blank" > 点击跳转</a >
图片(body) 拿博客背景图举例:
<img src ="https://typora-666.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/imaes/202407282152220.png" />
如果想导入自己本地的图片,要填写相对路径
<img src ="/static/xxx.jpg" />
如果想要设置图片的高度和宽度,要在地址后面加上style关键字
<img src ="https://typora-666.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/imaes/202407282152220.png" style ="width: 100px;height: 100px;" />
也可以按比例设置
<img src ="https://typora-666.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/imaes/202407282152220.png" style ="width: 50%;" />
小结 列表(body) <ul > <li > test1</li > <li > test2</li > <li > test3</li > </ul >
实现的是一个无序号列表也就是markdown里面的
<ol > <li > test1</li > <li > test2</li > <li > test3</li > </ol >
实现的是一个有序号列表
test1 test2 test3 u和o分别指unordered和ordered,<li>属于块级标签
表格(body) <table > <thead > <tr > <th > name</th > <th > age</th > <th > sex</th > </tr > </thead > <tbody > <tr > <td > 张三</td > <td > 18</td > <td > 男</td > </tr > <tr > <td > 李四</td > <td > 19</td > <td > 男</td > </tr > <tr > <td > 王五</td > <td > 20</td > <td > 女</td > </tr > </tbody > </table >
嵌套有点多,一一来解释
<table>标签用来表明这是一个表标签<thead>即table head,用来指示表头<tbody>即table body,用来指示表的主体<tr>即table row,用来指示表的一行<th>和<td>分别用来指示表头和表主体的一列如果想加一个边框,可以添加border关键字
<table border ="1" > <thead > <tr > <th > name</th > <th > age</th > <th > sex</th > </tr > </thead > <tbody > <tr > <td > 张三</td > <td > 18</td > <td > 男</td > </tr > <tr > <td > 李四</td > <td > 19</td > <td > 男</td > </tr > <tr > <td > 王五</td > <td > 20</td > <td > 女</td > </tr > </tbody > </table >
input系列(body) <input type ="text" /> <input type ="password" /> <input type ="file" /> <input type ="radio" name ="n1" /> 男<input type ="radio" name ="n1" /> 女<input type ="checkbox" /> 唱<input type ="checkbox" /> 跳<input type ="checkbox" /> rap<input type ="checkbox" /> 篮球<input type ="button" value ="按钮" /> <input type ="submit" value ="提交" />
text类型为一个文本框password类型输入时会把输入内容变成黑点file类型生成一个选择文件的按钮radio类型会生成一个小圆点供选择,只有当两个radio的name是一样时才可以二选一,否则都可以选,但大多时候选择单选checkbox类型则是复选框,可以选多个button类型则是一个按钮submit类型也是一个按钮,但是它可以提交表单结果如图:
由此可见,input标签也是一个内联标签
下拉框(body) <select > <option > 北京</option > <option > 上海</option > <option > 广州</option > <option > 深圳</option > </select > <select multiple > <option > 北京</option > <option > 上海</option > <option > 广州</option > <option > 深圳</option > </select >
<select>定义一个下拉框,<option>里面存放选择项,如果添加了multiple关键字,则可以多选,长按鼠标左键即可。
多行文本输入 <textarea>用于定义一个用户可以多行输入的文本框,用户还可以自行拖动文本框尺寸,加入row关键字可以定义默认输入行数
<textarea rows ="3" > </textarea >
默认显示一个高度为3行的文本框,但用户输入的行数可以大于3且可以拖动
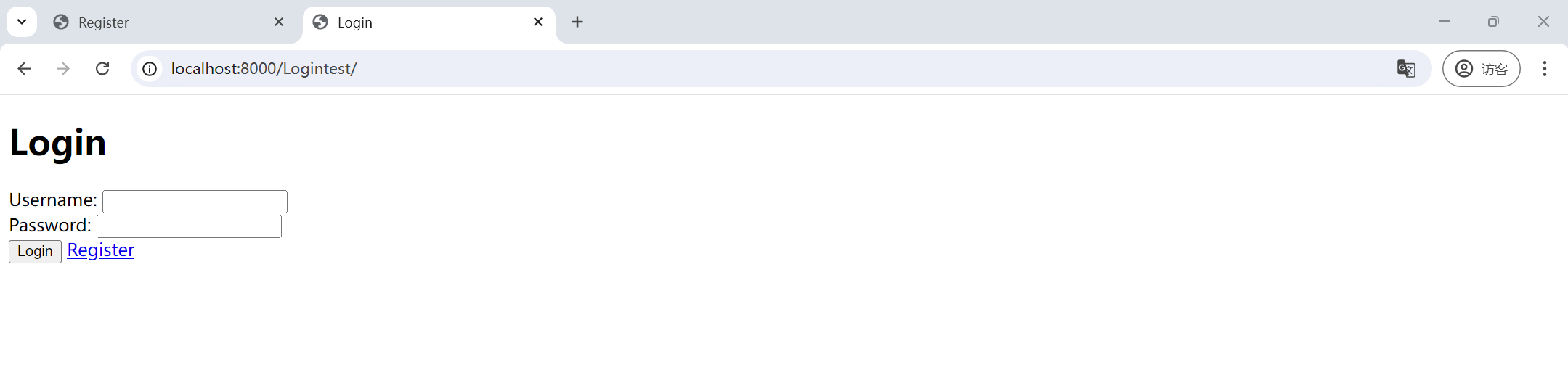
案例一:用户登录与注册界面 配合python里面的web框架,简略的制作一个用户登录与注册页面。这里以django为例,想了解django的伙伴可以看这篇文章
Django实践
案例要求:实现一个简略的与登录与注册界面
案例思路:
需要两个界面,localhost:8000/Logintest和localhost:8000/register,所以在urls.py里面定义两个页面
from django.contrib import adminfrom django.urls import pathfrom web.views import * urlpatterns = [ path("admin/" , admin.site.urls), path("login/" , login), path("user/" , user), path("Logintest/" ,Logintest), path("register/" ,register) ]
实现这两个页面的逻辑,这里要介绍一个新的标签<form>,这个是表单标签,之前提到的submit类型的input标签就是用来提交这个表单标签的。有两个关键的字段:action和method。action:定义将表单提交到哪个路由(url)method:定义提交表单的方法,一般有GET和POST两种:
GET:一般用来获取数据,提交的数据一般在放在URL中,安全性比较差。常见会有一个?(query提示符)接上提交的参数,例如在浏览器搜索的时候,会把搜索的东西放到URL里面去POST:一般用来提交数据,提交的数据不会在URL显示出来,提交的数据是放在数据包的body字段了解了上述知识之后就可以开始编写html文件了,在web(自己的app名字)/templates文件夹下编写Logintest.html
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <title > Login</title > </head > <body > <h1 > Login</h1 > <form action ="/Logintest/" method ="post" > {% csrf_token %} <div > <span > Username: <input type ="text" name ="username" /> </span > </div > <div > <span > Password: <input type ="password" name ="password" /> </span > </div > <div > <input type ="submit" value ="Login" /> <span > <a href ="/register" > Register</a > </span > </div > <div > {{message}} </div > </form > </body > </html >
这里面有一个 {% csrf_token %},是django所采用的一种防御措施,必须要有对应的token才能访问。为了防止**跨站请求伪造(CSRF)**攻击,通常需要在表单中包含 CSRF 令牌。可以使用 Django 提供的模板标签 {% csrf_token %} 来实现这一点。这里要提交数据就用post请求了,如果用get请求,username和password会显示在url中,可能导致泄露个人信息。
编写register.html文件如下
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <title > Register</title > </head > <body > <h1 > Register</h1 > <form action ="/register/" method ="post" > {% csrf_token %} <div > <span > Username: <input type ="text" name ="username" /> </span > </div > <div > <span > Password: <input type ="password" name ="password" /> </span > </div > <div > <input type ="submit" value ="Register" /> </div > <div > {{message}} </div > </form > </html >
接下来就要编写视图函数来实现登录和注册的逻辑,由于一般网页请求是get请求,首先判断网页是不是post请求,如果不是就直接返回html页面,如果是post请求,就判断输入的username和password是否合法,输出对应的html以及message信息views.py
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirectdef Logintest (request ): if request.method == "POST" : username = request.POST.get("username" ) password = request.POST.get("password" ) if username in user_list and password in password_list: return render(request, "login1.html" ,{"message" :"登录成功" }) else : return render(request, "login1.html" ,{"message" :"用户名或密码错误" }) else : return render(request, "Logintest.html" ) user_list = ["admin" ] password_list = ["admin" ] def register (request ): if request.method == "POST" : username = request.POST.get("username" ) password = request.POST.get("password" ) if username and password: user_list.append(username) password_list.append(password) print (user_list) print (password_list) return render(request, "register.html" ,{"message" :"注册成功" }) else : return render(request, "register.html" ,{"message" :"注册失败" }) else : return render(request, "register.html" )
由于还没介绍数据库,先用列表来存一下用户名和密码来简略判断一下是否能登录。
最终结果如图:
CSS样式 应用方式 在标签上 <img src ="..." style: "height: 100px " /> <div style ="color: red" > hello world </div >
在head标签上 <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <style > .c1 { color : red; } </style > </head >
这种写法相当于定义了一个style类,之后要调用直接调用这个类即可
<h1 class ="c1" > hello world </h1 >
写到文件中 编写test.css文件如下:
.c1 { height : 100px ; } .c2 { color : red; }
要导入css文件则需要在html文件head标签里面添加link
<head > <link rel ="stylesheet" href ="test.css" /> </head >
选择器 CSS有多种选择器
类选择器
<style > .c1 { color : red; } </style > <div class ="c1" > hello world </div >
选择的时候用class来选择哪一个样式
ID选择器
<style > #c2 { color : green; } </style > <div id ="c2" > hello world </div >
选择的时候用id来选择,与类选择器的不同的是,选择id的标签应该是唯一的 ,但是选择类的标签可以有多个。对于同一个id选择器#c2,例如
<h2 id ="c2" > Test </h2 > <div id ="c2" > Test </div >
是不合法的,但是浏览器还是会显示同一个样式,但是可能导致程序出现未知错误
标签选择器
所有的div标签包裹的内容全部变为绿色
属性选择器
<style > input [type="text" ] { border : 1px solid red; } </style > <input type ="text" >
所有的text类型的输入框全部变成红色
后代选择器
<style > li { color : yellow; } .test li { color : pink; } </style > <li > test1</li > <li > test2</li > <li > test3</li > <span class ="test" > <li > test4</li > <li > test5</li > <li > test6</li > </span >
其中先定义了一个li的标签选择器,又定义了一个后代选择器,只有class为test的li标签包裹的内容才显示粉色。
如果有多级标签,如
<style > .test > a { color : purple; } </style > <span class ="test" > <a > test6 <div > <a > test7 </a > </div > </a > </span >
.test > a是只对最外层的a标签有效,而对里面的a标签没有用,上述显示的结果就是test6为紫色,test7为黑色。
特性
<style > .c1 { color : red; border : 1px solid red; } .c2 { color : blue; } </style > <span class ="c1 c2" > hello world </span >
这会显示一个红色边框颜色为蓝色的hello world
如果不想让其覆盖可以在覆盖的地方添加一项!important
.c1 { color: red !important; border: 1px solid red; }
高度和宽度 通过设置height和width来调整高度和宽度,例如
.hw { height: 100px; width: 100px; }
但是发现这个比较鸡肋。
对于块级标签,无论设置设置宽度为多少,它始终占一行,就算宽度比较小,其他内容也不能和它并排显示。
而对于内联标签,高度和宽度全部没用,无论设置多少,所占大小都是字体大小。
于是,接下来介绍一个css里面改变块级标签和内联标签的方法
块级标签和内联标签 div { display: inline-block; } .hw { height: 100px; width: 100px; } <div class ="hw" > hello world </div > <div class ="hw" > hallow word </div >
这段代码将div这个块级标签转变为内联-块级标签 ,顾名思义就是继承了块级和内联标签的特性。它既可以像内联标签一样在一行显示 ,又继承了块级标签可以修改高度和宽度 的特性。
并且也可以通过display将块级标签和内联标签互换
div { display: inline; } span { display: block; }
这样就完成了两种标签的特性互换~~(好玩吧,嘿嘿)~~
字体和颜色 .c1 { color: red; font-size: 58px; font-weight: 600; font-family: Microsoft YaHei; font-style: italic; }
color:除了用英文单词也可以接#xxxxxx,x表示16进制数font-size:定义字体的大小font-weight:定义字体的粗细font-family:定义字体font-style:定义字体是否倾斜文字对齐方式 .hw { text-align: center; line-height: 100px; height: 100px; width: 100px; }
text-align:定义文本的位置line-height:定义某一行的高度,这里设置为height值表示在高度上面居中浮动 对于以下的span标签,显示出来的hello world是挨着的。
<span > hello </span > <span > world </span >
如果想要world浮动到最右边,那么就需要用float来控制
<span > hello </span > <span style ="float: right;" > world </span >
浮动特性比较绕,下面推荐一篇文章介绍浮动的原理与清除CSS浮动(float,clear)通俗讲解
内边距 .outer { height: 200px; width: 200px; border: 1px solid red; padding-top: 20px; padding-right: 20px; padding-bottom: 20px; padding-left: 20px; } <div class ="outer" > test </div >
通过padding将定义的一个border撑大
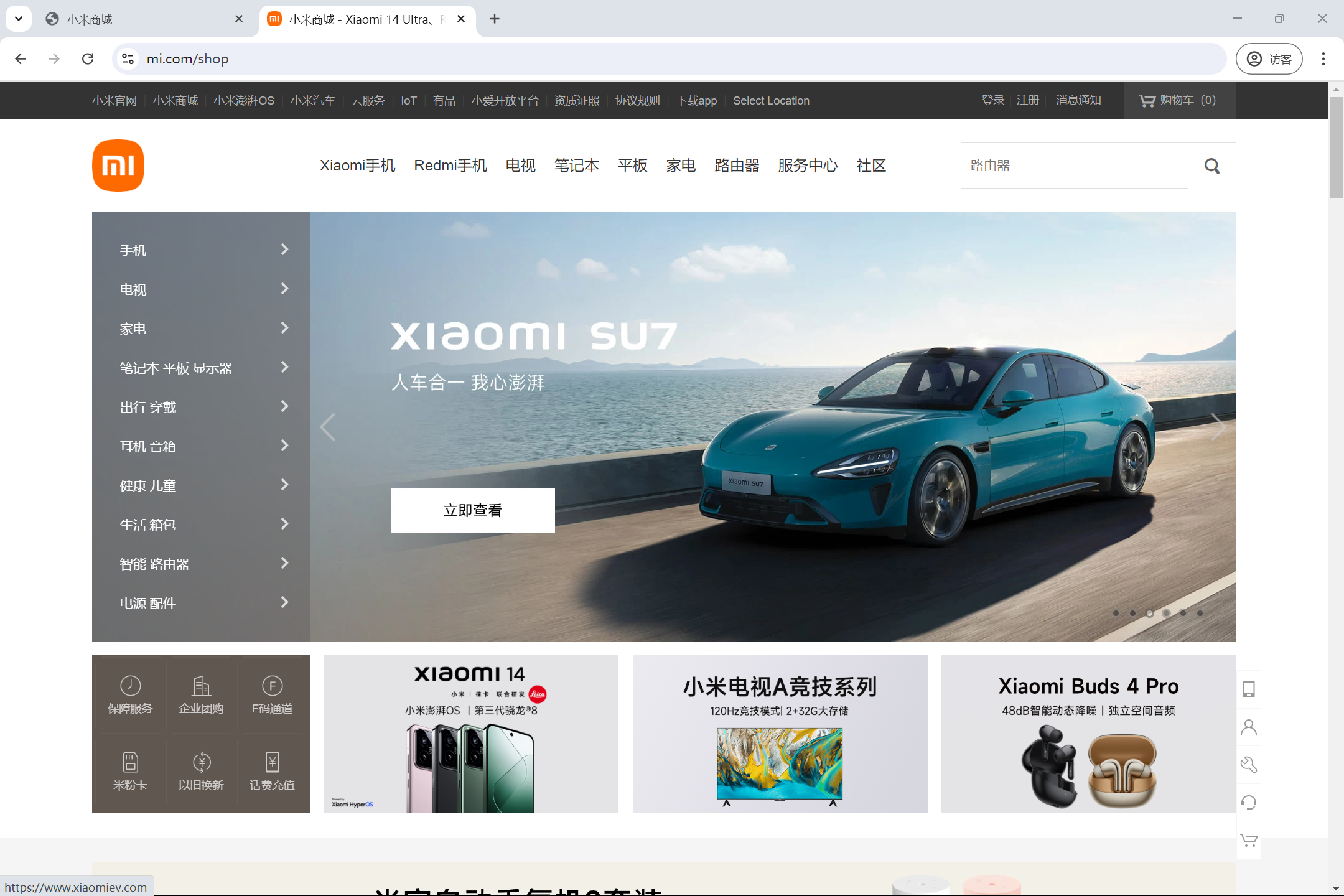
案例二:小米商城导航栏界面 对比效果如图:
编写html文件如下
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <title > 小米商城</title > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <style > body { margin : 0 ; } .menu { height : 40px ; background-color : #333 ; font-size : 12px ; } .menu .container { width : 1226px ; margin : 0 auto; } .menu .container a { height : 40px ; color : #b0b0b0 ; line-height : 40px ; text-decoration : none; display : inline-block; } .menu .container a :hover { color : #fff ; } .menu .container .func-left a { float : left; } .menu .container .func-left .sep { float : left; color : #424242 ; width : 3.23px ; height : 16px ; line-height : 40px ; margin : 0 3.6px ; } .menu .container .func-right a { float : right; } .menu .container .func-right .sep { float : right; color : #424242 ; width : 3.23px ; height : 16px ; line-height : 40px ; margin : 0 3.6px ; } .menu .container .func-right .shopcar { background-color : #424242 ; width : 120px ; height : 40px ; display : block; text-align : center; } .submenu .container { height : 100px ; width : 1226px ; margin : 0 auto; } .submenu .container .left .logo { height : 56px ; width : 56px ; margin-top : 22px ; float : left; } .submenu .container .right { color : #333333 ; padding : 12px 0 0 30px ; font-size : 14px ; width : 1140px ; height : 88px ; margin : 0 ; float : left; } .submenu .container .right .blank { height : 88px ; width : 127px ; padding : 0 15px 0 0 ; float : left; } .submenu .container .right a { float : left; color : #333333 ; font-size : 16px ; padding : 26px 10px 38px ; text-decoration : none; } .submenu .container .right a :hover { color : #ff6700 ; } .submenu .container .right .search { float : right; width : 300px ; height : 40px ; margin-top : 20px ; } .content { width : 1226px ; margin : 0 auto; } .content img { width : 100% ; height : 100% ; } .subcontent { padding-top : 10px ; } .subcontent .container { height : 200px ; width : 1226px ; margin : 0 auto; } .subcontent .container .func { height : 170px ; width : 237px ; float : left; background-color : #665e57 ; } .subcontent .container .func .item { width : 79px ; height : 85px ; text-align : center; float : left; } .subcontent .container .item .example { height : 170px ; width : 316PX ; padding-left : 12px ; float : right; } .subcontent .container .func .item .des { color : #fff ; font-size : 14px ; } .subcontent .container .func .item a { text-decoration : none; text-align : center; opacity : 0.7 ; } .subcontent .container .func .item a :hover { opacity : 1 ; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="menu" > <div class ="container" > <div class ="func-left" > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > 小米官网</a > <div class ="sep" > |</div > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > 小米商城</a > <div class ="sep" > |</div > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > 小米澎湃OS</a > <div class ="sep" > |</div > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > 小米汽车</a > <div class ="sep" > |</div > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > 云服务</a > <div class ="sep" > |</div > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > loT</a > <div class ="sep" > |</div > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > 有品</a > </div > <div class ="func-right" > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" class ="shopcar" > 购物车(0)</a > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > 消息通知</a > <div class ="sep" > |</div > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > 注册</a > <div class ="sep" > |</div > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > 登录</a > </div > <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </div > </div > <div class ="submenu" > <div class ="container" > <div class ="left" > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <img src ="https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi.com-assets/shop/img/logo-mi2.png " class ="logo" /> </a > </div > <div class ="right" > <div class ="blank" > </div > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <span > Xiaomi手机</span > </a > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <span > Redmi手机</span > </a > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <span > 电视</span > </a > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <span > 笔记本</span > </a > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <span > 家电</span > </a > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <span > 路由器</span > </a > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <span > 服务中心</span > </a > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <span > 社区</span > </a > <div class ="search" > <input type ="button" value ="🔍" style =" height: 41px; float: right;" /> <input type ="text" placeholder ="搜索商品名称" style ="height: 35px;float: right;" /> </div > </div > </div > </div > <div class ="content" > <div class ="container" > <img src ="https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/397f2569b126d8fba446b6bbf57ef771.jpg?thumb=1&w=1839&h=690&f=webp&q=90" /> <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </div > <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </div > <div class ="subcontent" > <div class ="container" > <div class ="func" > <div class ="item" > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <img src ="https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/82abdba456e8caaea5848a0cddce03db.png?w=48&h=48" alt ="" style ="height: 24px;width: 24px;display: block;margin: 0 auto;margin-top: 18px;" > <span class ="des" > 保障服务</span > <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </a > </div > <div class ="item" > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <img src ="https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/82abdba456e8caaea5848a0cddce03db.png?w=48&h=48" alt ="" style ="height: 24px;width: 24px;display: block;margin: 0 auto;margin-top: 18px;" > <span class ="des" > 保障服务</span > <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </a > </div > <div class ="item" > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <img src ="https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/82abdba456e8caaea5848a0cddce03db.png?w=48&h=48" alt ="" style ="height: 24px;width: 24px;display: block;margin: 0 auto;margin-top: 18px;" > <span class ="des" > 保障服务</span > <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </a > </div > <div class ="item" > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <img src ="https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/82abdba456e8caaea5848a0cddce03db.png?w=48&h=48" alt ="" style ="height: 24px;width: 24px;display: block;margin: 0 auto;margin-top: 18px;" > <span class ="des" > 保障服务</span > <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </a > </div > <div class ="item" > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <img src ="https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/82abdba456e8caaea5848a0cddce03db.png?w=48&h=48" alt ="" style ="height: 24px;width: 24px;display: block;margin: 0 auto;margin-top: 18px;" > <span class ="des" > 保障服务</span > <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </a > </div > <div class ="item" > <a href ="https://www.mi.com/index.html" > <img src ="https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/82abdba456e8caaea5848a0cddce03db.png?w=48&h=48" alt ="" style ="height: 24px;width: 24px;display: block;margin: 0 auto;margin-top: 18px;" > <span class ="des" > 保障服务</span > <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </a > </div > <div style ="clear: both;" > </div > </div > <div class ="item" > <img src =" https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/1ac77590368ff636d0b4f6a988133f55.png?w=632&h=340" alt ="" class ="example" /> </div > <div class ="item" > <img src =" https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/8dede2520f8dfff9c9b690af498cafe8.jpg?w=632&h=340" alt ="" class ="example" /> </div > <div class ="item" > <img src =" https://cdn.cnbj1.fds.api.mi-img.com/mi-mall/6b67117bc92924fb2ff0e7ad2be86084.png?w=632&h=340" alt ="" class ="example" /> </div > </div > </div > </body > </html >
补充知识点 body无边框 当把宽度设置到100%时,发现浏览器的两边还是出现了白边,这是因为body 有默认的margin-left和margin-right,要去掉白边,设置style如下
<style > body { margin : 0 ; } </style >
hover 可以自定义当鼠标放在hover所描述的标签上的行为。例如上述鼠标放在顶部菜单栏的导航上字体会变白,放在二级菜单导航上字体会变橙色等。
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <title > Test</title > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <style > .c1 { color : red; font-size : 20px ; } .c1 :hover { color : blue; font-size : 50px ; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="c1" > hello world </div > </body > </html >
此案例当鼠标放在hello world上面时,字体会变蓝并且变大
after 可以在已定义标签的后面进行一些操作
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <title > Test</title > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <style > .c1 :after { content : " world" ; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="c1" > hello</div > <div class ="c1" > hi</div > </body > </html >
此示例在运用c1样式的标签后面加上了 world 还有一个比较使用的用法
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <title > Test</title > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <style > .clearfix :after { content : "" ; display : block; clear : both; } </style > </head > <body > <div > <div class ="item" > 1</div > <div class ="item" > 2</div > <div class ="item" > 3</div > </div > </body > </html >
定义了一个clearfix的样式,便于我们去清除浮动。
opacity 用于设置颜色的透明度,如案例二左下角的保障服务,其实是白色设置了透明度为0.7
.subcontent .container .func .item a { text-decoration: none; text-align: center; opacity: 0.7; }
position fixed 固定在窗口的某个位置,最常见的示例是返回顶部
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <title > Test</title > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <style > body { margin : 0 ; } .c1 { position : fixed; right : 10px ; bottom : 10px ; width : 60px ; height : 60px ; border : 1px solid red; } .c2 { height : 10000px ; width : 100% ; background-color : #333333 ; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="c1" > </div > <div class ="c2" > </div > </body > </html >
以上示例会在屏幕右下角显示一个红色的框,无论上下怎么滑动,相对于屏幕来说,边框都是固定的
relative和absolute(联合使用) 如果不想要标签相对屏幕的位置,而想要一个标签依赖于另一个标签的位置,就可以使用relative和absolute 例如
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <title > Test</title > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <style > .c1 { position : relative; width : 500px ; height : 500px ; left : 100px ; top : 100px ; border : 1px solid red; } .c2 { position : absolute; height : 100px ; width : 100px ; background-color : #333333 ; top : 50px ; left : 50px ; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="c1" > <div class ="c2" > </div > </div > </body > </html >
以上实例发现红框的位置是相对于浏览器边框而言,而灰色矩形的位置是相对红框边界而言。
运用所学知识就可以构建出小米商城下载app的示例
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <title > Test</title > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <style > .app { height : 10px ; width : 100px ; text-align : center; } .app .download { position : relative; width : 100px ; } .app .download img { height : 90px ; width : 90px ; position : absolute; top : 20px ; left : 0 ; display : none; } .app :hover { color : #ff6700 ; } .app :hover .download img { display : block; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="app" > <div class ="download" > 下载app <img src ="https://i1.mifile.cn/f/i/17/appdownload/download.png?1" alt ="" > </div > </div > </body > </html >
鼠标移动到下载app时会弹出二维码,当然淡入淡出的效果是js实现的,暂不考虑。
总结 至此,有关CSS 样式最重要的一些知识点已经罗列完毕,当然这只是CSS 样式的冰山一角,总结下来,发现写页面只有两个字:丑、累。接下来,要介绍前端最后一个要素:JavaScript
JavaScript 代码位置 head标签里面,style标签下面body标签尾部(推荐)<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <style > ... </style > <script type ="text/javascript" > ... </script > </head > <body > <div > <h1 > 标题</h1 > <p > 内容</p > </div > <script type ="text/javascript" > ... </script > </body > </html >
代码存在形式 写在HTML页面中,如上述代码
写在文件里面,在HTML里面导入(和CSS类似)
<script src ="/static/my.js" > </script >
注释 HTML的注释
CSS的注释(只能写在style里面)
Javascript(只能写在script里面)
变量定义 输出 需要在浏览器的console里面查看
字符串类型 var name = "张三" ;var name = String ("张三" )
var name = "张三" ;var v1 = name.length ; var v2 = name[0 ]; var v3 = name.trim (); var v4 = name.substring (0 ,1 );
案例:跑马灯 <script type="text/javascript" > function show ( var text = document .getElementById ('text' ); var textContent = text.innerText ; var first = textContent[0 ]; var other = textContent.substring (1 ,textContent.length ); var newtext = other + first; text.innerText = newtext; } setInterval (show, 1000 ); </script>
此案例实现了"欢迎来到我的博客"的滚动效果
数组 var v1 = [11 ,22 ,33 ,44 ];var v1 = Array ([11 ,22 ,33 ,44 ]);
var v1 = [11 ,22 ,33 ,44 ];v1[1 ] v1[0 ] = 55 ; v1.push (66 ); v1.pop (); v1.unshift (77 ); v1.shift (); v1.splice (1 ,0 ,88 ); v1.splice (1 ,2 );
案例:动态数组 <!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > </head > <body > <script type ="text/javascript" > var hobby = ["唱" ,"跳" ,"rap" ,"篮球" ]; var ul = document .createElement ("ul" ); for (var i in hobby) { var text = hobby[i]; var li = document .createElement ("li" ); li.innerText = text; ul.appendChild (li); } document .body .appendChild (ul); </script > </body > </html >
本案例实现了自动创建ul以及编辑li标签的内容的功能
字典 <!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <style > table , th , td { border : 1px solid black; } </style > </head > <body > <script type ="text/javascript" > var table = document .createElement ("table" ); var thead = document .createElement ("thead" ); table.appendChild (thead); var tbody = document .createElement ("tbody" ); table.appendChild (tbody); var thr = document .createElement ("tr" ); thead.appendChild (thr); var th = document .createElement ("th" ); th.innerHTML = "姓名" ; thr.appendChild (th); th = document .createElement ("th" ); th.innerHTML = "年龄" ; thr.appendChild (th); th = document .createElement ("th" ); th.innerText = "性别" ; thr.appendChild (th); var info = { name : "张三" , age : 18 , gender : "男" }; var tbr = document .createElement ("tr" ); for (var key in info) { var td = document .createElement ("td" ); td.innerText = info[key]; tbr.appendChild (td); } tbody.appendChild (tbr); document .body .appendChild (table); </script > </body > </html >
本案例结合了css以及javascript创建了一个table,但是表格只能读取一个数据,如果字典里面有多个数据,需要使用二重循环。如下:
<!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <style > table , th , td { border : 1px solid black; border-collapse : collapse; } </style > </head > <body > <script type ="text/javascript" > var table = document .createElement ("table" ); var thead = document .createElement ("thead" ); table.appendChild (thead); var tbody = document .createElement ("tbody" ); table.appendChild (tbody); var thr = document .createElement ("tr" ); thead.appendChild (thr); var th = document .createElement ("th" ); th.innerHTML = "姓名" ; thr.appendChild (th); th = document .createElement ("th" ); th.innerHTML = "年龄" ; thr.appendChild (th); th = document .createElement ("th" ); th.innerText = "性别" ; thr.appendChild (th); var info =[ { name : "张三" , age : 18 , gender : "男" }, { name : "李四" , age : 19 , gender : "男" }, { name : "王五" , age : 20 , gender : "女" } ]; for (var inx in info) { var one_info = info[inx]; var tbr = document .createElement ("tr" ); for (var key in one_info) { var td = document .createElement ("td" ); td.innerText = one_info[key]; tbr.appendChild (td); } tbody.appendChild (tbr); } document .body .appendChild (table); </script > </body > </html >
条件语句 if (条件) {} else if (条件) { }
函数 function func ( ... } func
DOM DOM,就是一个模块,可以对HTML页面中的标签进行操作。
var tag = document .getElementById ("xx" );tag.innerText tag.innerText = "hello world" ; var tag = document .createElement ("xxx" );tag.innerText = "hello world" ;
事件的绑定 <!DOCTYPE html > <html > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <style > </style > </head > <body > <input type ="text" placeholder ="请输入内容" id ="content" > <input type ="button" value ="打印" onclick ="printContent()" > <ul id ="ul" > </ul > <script type ="text/javascript" > function printContent ( var tagcontent = document .getElementById ("content" ); var content = tagcontent.value ; if (content.trim () == "" ) { alert ("请输入内容" ); tagcontent.value = "" ; return ; } var ul = document .getElementById ("ul" ); var li = document .createElement ("li" ); li.innerText = content; ul.appendChild (li); tagcontent.value = "" ; } </script > </body > </html >
上述示例完成了将用户输入的内容打印到html页面上。其中
<input type ="button" value ="打印" onclick ="printContent()" >
onclick为鼠标单击事件。
ps :DOM有许多内容,但实际开发中不需要自己编写。常用jQuery / vue.js / react.js 来辅助开发
jQuery jQuery是一个JavaScript的第三方模块(第三方类库)。
Bootstrap 别人已经写好的CSS 样式,使用方法:
下载BootStrap
引入bootStrap
<link rel ="stylesheet" href ="static/css/bootstrap.css" >
href填写存放BootStrap的路径
在官网寻找需要的组件并cv